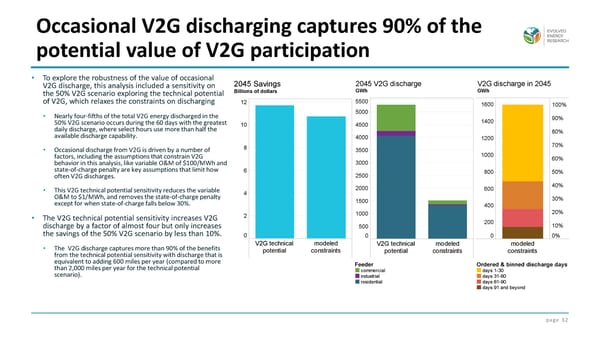
page 32 • To explore the robustness of the value of occasional V2G discharge, this analysis included a sensitivity on the 50% V2G scenario exploring the technical potential of V2G, which relaxes the constraints on discharging • Nearly four-fifths of the total V2G energy discharged in the 50% V2G scenario occurs during the 60 days with the greatest daily discharge, where select hours use more than half the available discharge capability. • Occasional discharge from V2G is driven by a number of factors, including the assumptions that constrain V2G behavior in this analysis, like variable O&M of $100/MWh and state-of-charge penalty are key assumptions that limit how often V2G discharges. • This V2G technical potential sensitivity reduces the variable O&M to $1/MWh, and removes the state-of-charge penalty except for when state-of-charge falls below 30%. • The V2G technical potential sensitivity increases V2G discharge by a factor of almost four but only increases the savings of the 50% V2G scenario by less than 10%. • The V2G discharge captures more than 90% of the benefits from the technical potential sensitivity with discharge that is equivalent to adding 600 miles per year (compared to more than 2,000 miles per year for the technical potential scenario). Occasional V2G discharging captures 90% of the potential value of V2G participation
 Exploring the Value of Vehicle to Grid (V2G) for California Page 31 Page 33
Exploring the Value of Vehicle to Grid (V2G) for California Page 31 Page 33